Russian forces struck civilian infrastructure and a military educational facility in Poltava City with two Iskander-M ballistic missiles, killing and wounding a significant number of people, as part of a wider strike series on the night of September 2 to 3. The Ukrainian Air Force reported that Russian forces launched three Iskander-M/North Korean KN-23 ballistic missiles from occupied Crimea, a Kh-59/69 cruise missile from Kursk Oblast, and 35 Shahed-136/131 drones from Kursk Oblast and occupied Cape Chauda, Crimea. The Ukrainian Air Force reported that Ukrainian forces downed 27 Shahed drones over Kyiv, Odesa, Kharkiv, Mykolaiv, Kherson, Poltava, Chernihiv, and Sumy oblasts, that six Shaheds did not strike their target, and that two Shahed drones flew toward Belgorod Oblast and occupied Donetsk Oblast. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky and Ukrainian Commander-in-Chief General Oleksandr Syrskyi reported that two Iskander missiles struck a military educational institution and a nearby hospital in Poltava City, partially destroying a building at the Poltava Military Communications Institute. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky stated the strike killed at least 51 and injured at least 271. Zelensky highlighted Ukraine's need for more air defense systems and interceptors and called on Western countries to lift restrictions on Ukrainian forces conducting long-range strikes against military targets within Russia as such restrictions inhibit Ukraine from defending against long-range Russian strikes. Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba told CNN on September 3 that only Patriot and SAMP/T air defense systems are capable of intercepting Russia's ballistic missiles. Russian milbloggers celebrated the strike and amplified footage of the strike and its aftermath.
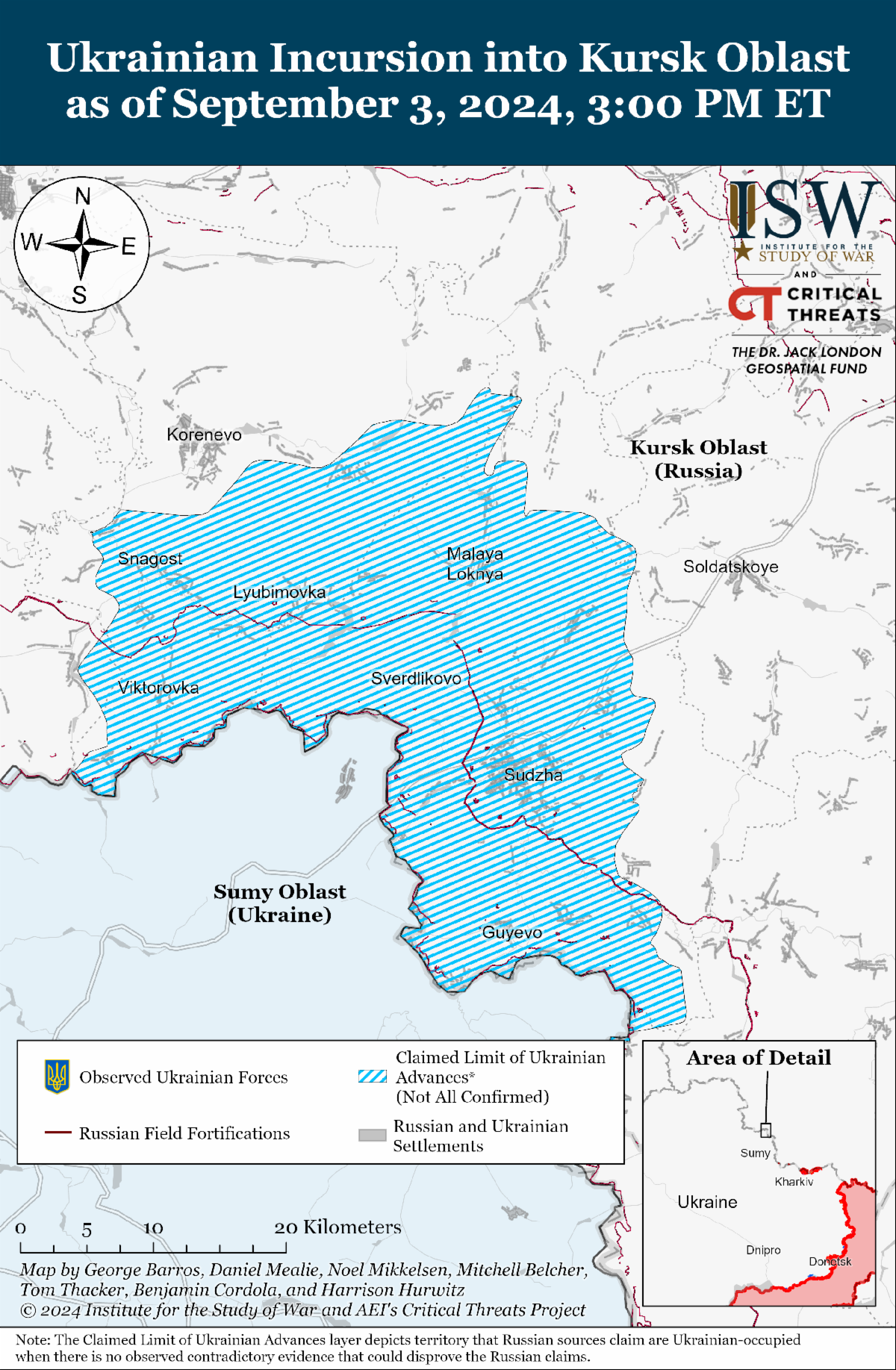
The wider impacts of the Ukrainian incursion into Kursk Oblast on the war and any envisioned diplomatic solution to the war are not yet clear, and assessments of these impacts are premature. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky stated during an interview with NBC on September 3 that Ukrainian forces are "conceptually" planning to hold territory in Kursk Oblast for an unspecified period of time, but did not offer further details about Ukraine's objectives for the incursion due to concerns about operational security. Zelensky reiterated that the Ukrainian incursion is an aspect of Ukraine's "victory plan" to end the war on just terms and bring Russia to the negotiating table. Zelensky noted that Ukraine intends to exchange Russian prisoners of war (POWs) captured in Kursk Oblast for Ukrainian POWs currently in Russian captivity and reiterated that one of the goals of the incursion was to force Russia to redeploy troops from the frontline throughout Ukraine, particularly eastern Ukraine. Zelensky stated that Russia has diverted roughly 60,000 troops from Ukraine to Kursk Oblast, and Ukrainian Commander-in-Chief General Oleksandr Syrskyi reported on August 27 that Russia has redeployed over 30,000 troops from the frontline in Ukraine to Kursk Oblast. ISW has observed indications for several weeks that the Russian military command was redeploying forces from northern Kharkiv Oblast, the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, and western Zaporizhia Oblast to Kursk Oblast and recently observed indications that the Russian military command is redeploying forces likely intended for future higher priority offensive operations in the Pokrovsk direction to Kursk Oblast. Russian President Vladimir Putin has thus far avoided redeploying the type of combat effective and experienced frontline units that will likely be necessary to push Ukrainian forces from Kursk Oblast, and Zelensky's statement suggests that Ukrainian forces will likely maintain positions in the over 1,100 square kilometers of territory where Ukrainian forces are reportedly operating in Kursk Oblast until Putin chooses to commit such forces. ISW assesses that Putin is attempting to preserve the Russian drive on Pokrovsk at the expense of delaying the clearing of Kursk but that the incursion is likely to have a variety of other important impacts on Russian military operations over various time periods regardless of its impact on the current Pokrovsk operation.
While the Ukrainian incursion into Kursk Oblast appears to be having operational-level impacts on the Russian military, the incursion has likely not yet shifted Putin's strategic-level thinking. ISW assesses that Putin maintains that Russia can slowly and indefinitely subsume Ukraine through grinding advances and that Russia can achieve its goals through a war of attrition against Ukrainian forces and by outlasting Western support for Ukraine — assessments that make Putin averse to peace negotiations on terms other than Ukrainian and Western capitulation to his demands.
Attempts to assess the impacts of the Ukrainian incursion at this premature stage will likely come to partial and inaccurate conclusions about Ukraine's ability to change the trajectory of the conflict and the Kremlin's appetite for peace negotiations on acceptable terms. Ukrainian counteroffensives in Fall 2022 both successfully pushed the frontline back from Kharkiv City – Ukraine's second largest city – and liberated Kherson City and established a defensible frontline along the Dnipro River. Ukraine demonstrated its ability to conduct operationally significant counteroffensive operations and liberate large swaths of territory when properly aided and equipped by the West in Fall 2022, and the assumption that Ukraine is permanently unable to conduct future counteroffensive operations that result in operationally significant gains with timely and reliable deliveries of Western aid is premature. Delays in the provision of Western aid, among other factors, hindered the Ukrainian 2023 counteroffensive and generated a military crisis in Ukraine in 2024 from which Ukraine is still attempting to recover. Russian forces were able to make tactically significant advances in northern Kharkiv Oblast and Donetsk Oblast in Spring and early Summer 2024 in large part because of the shortages of artillery and air defense munitions caused by the suspension of US military assistance. ISW continues to assess that prompt and reliable Western security assistance will be critical to Ukraine's ability to conduct future counteroffensive operations, and that the US and wider Western alliance can make decisions to redress Ukrainian materiel constraints caused by delays in Western security assistance.
Key Takeaways:
- Russian forces struck civilian infrastructure and a military educational facility in Poltava City with two Iskander-M ballistic missiles, killing and wounding a significant number of people, as part of a wider strike series on the night of September 2 to 3.
- The wider impacts of the Ukrainian incursion into Kursk Oblast on the war and any envisioned diplomatic solution to the war are not yet clear, and assessments of these impacts are premature.
- Attempts to assess the impacts of the Ukrainian incursion at this premature stage will likely come to partial and inaccurate conclusions about Ukraine's ability to change the trajectory of the conflict and the Kremlin's appetite for peace negotiations on acceptable terms.
- Reuters reported that the US is considering providing Ukraine with long range Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missiles (JASSMs) but that Ukraine would not receive the missiles for months.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin concluded his trip to Mongolia by signing agreements that strengthen bilateral economic ties and trilateral energy relations between Russia, Mongolia and the People's Republic of China (PRC).
- South African President Cyril Ramaphosa and People's Republic of China (PRC) President Xi Jinping issued a joint statement praising each other’s purported efforts to address the war in Ukraine.
- Russian forces recently advanced near Toretsk and Pokrovsk and southwest of Donetsk City.
- Russian occupation authorities continue to advertise Russian military service to civilians in occupied Ukraine.
| 




 [ISW] 러시아의 공세 캠페인 평가, 2024년 9월 7일
[ISW] 러시아의 공세 캠페인 평가, 2024년 9월 7일
 [ISW] 러시아의 공세 캠페인 평가, 2024년 8월 31일
[ISW] 러시아의 공세 캠페인 평가, 2024년 8월 31일