The Kremlin's recent economic policies indicate that the Russian economy will likely face significant challenges in 2025 and that Russian President Vladimir Putin is worried about Russia's economic stability in the long term. The Kremlin recently adopted several policies that aim to cut Russian government spending on wounded Russian servicemen, combat inflation, and address long-term demographic problems such as low birth rates and labor shortages. These policies demonstrate that the Russian economy is not as resilient to Western sanctions, monetary constraints, and the cost of the war effort as the Russian government postures. These policies also demonstrate that the Kremlin will not be able to sustain the protracted war effort for years and decades to come while shielding Russian society from economic challenges. Consistent Western and international support for Ukraine's resistance on the battlefield will further exacerbate Russia's economic problems.
Putin modified compensation promised for Russian servicemen wounded while fighting in Ukraine — a clear indicator that the Kremlin is trying to cut the mounting short- and long-term costs of the war and restore balance to the Russian economy. Putin controversially changed Russian policy guaranteeing a one-time payment of three million rubles ($30,124) to all Russian servicemen who have been wounded in combat in Ukraine since March 2022. Putin signed a decree on November 13 that restricted the one-time payments of three million rubles only to servicemen who sustained serious injuries in combat, only offering one million rubles ($10,152) to lightly wounded servicemen, and 100,000 rubles ($1,015) to servicemen who sustained minor injuries on the battlefield. Putin's decree generated significant backlash from the Russian ultranationalist milblogger community, and Putin attempted to placate this community on November 14 by increasing the one-time payments to four million rubles ($40,136), but still only for Russian servicemen who sustain severe battlefield injuries that result in a disability. A Russian milblogger noted that Putin's authorization to increase compensation for disabled servicemen does not alter the fact that the Kremlin is reneging on promises to thousands of Russian servicemen who joined the Russian military solely due to large financial incentives. The milblogger added that Russian military medical commissions are also becoming increasingly — and often deliberately unfairly — selective in diagnosing Russian servicemen with severe injuries.
Putin originally introduced the policy offering all wounded Russian servicemen three million rubles to incentivize military recruitment after he had decided against declaring general mobilization in Spring 2022. Financial incentives became the key pillar of the Russian military's recruitment campaign and personnel retention efforts over the past nearly three years, and the reversal of such incentives indicates that the system is becoming economically unsustainable for the Kremlin. ISW notably assessed in Summer 2022 that the Kremlin's reliance on high financial incentives for force generation was committing Russia to short- and long-term financial responsibilities to thousands of Russians, such as paying veterans pensions, compensations to families of deceased servicemen, and other state benefits.
Key Takeaways:
- The Kremlin's recent economic policies indicate that the Russian economy will likely face significant challenges in 2025 and that Russian President Vladimir Putin is worried about Russia's economic stability in the long term.
- Putin modified compensation promised for Russian servicemen wounded while fighting in Ukraine — a clear indicator that the Kremlin is trying to cut the mounting short- and long-term costs of the war and restore balance to the Russian economy.
- The Kremlin's efforts to combat inflation and high interest rates are also reportedly impacting the expansion of the Russian defense industrial base (DIB) and prospects for mobilizing the economy.
- The Russian DIB is unlikely to match the production rate necessary to replace Russian weapons losses under these monetary policies.
- The Kremlin is also adopting policies aimed at bolstering the domestic population in the long term, signaling mounting concerns over declining demographics and labor shortages that could threaten the sustainable operations of the Russian DIB.
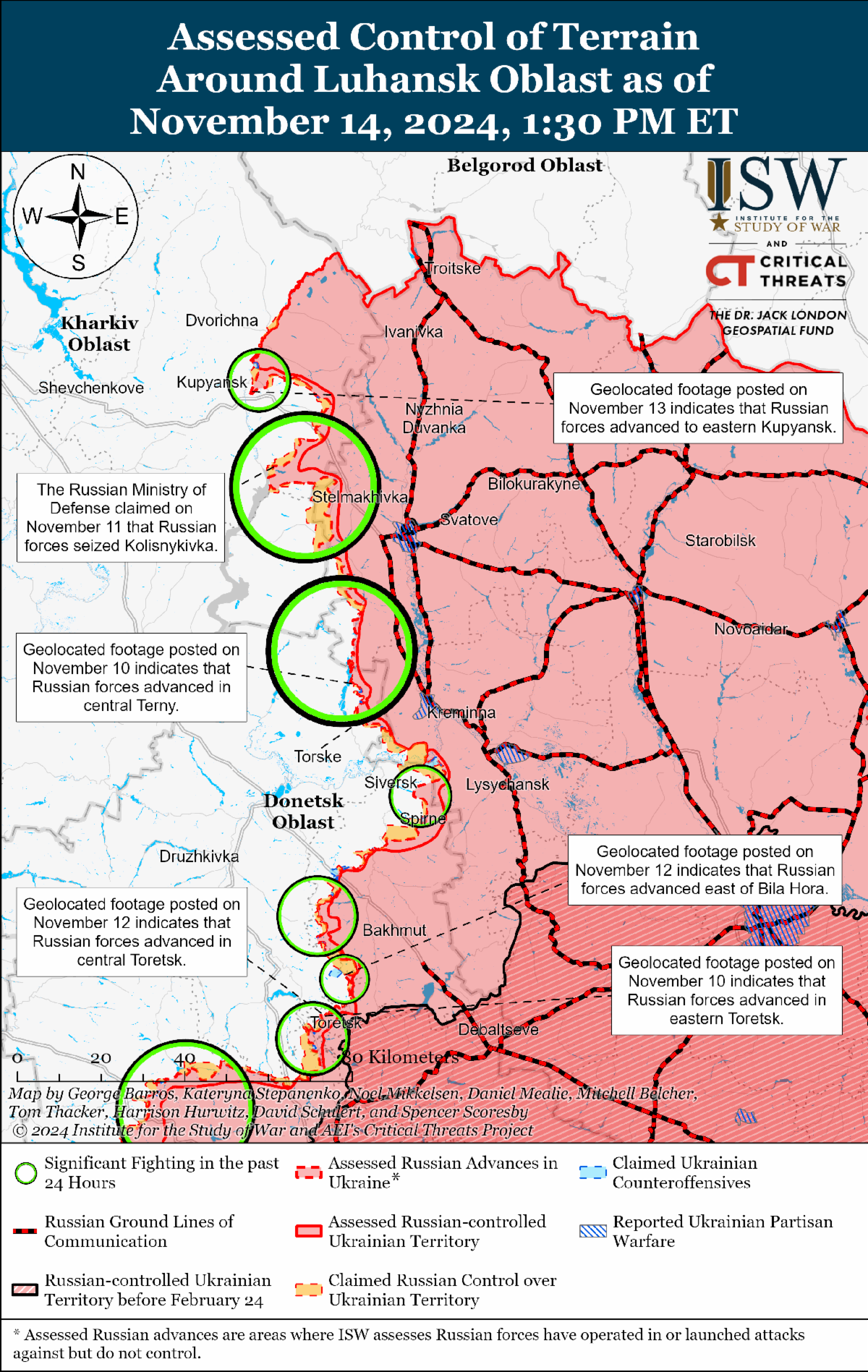
- Russian forces recently advanced into Kupyansk during a likely roughly company-sized mechanized assault, although ISW does not assess that Russian forces control the area.
- A recent Russian state-affiliated poll suggests that most Russian residents feel largely unaffected by the war in Ukraine, supporting reports of growing concerns among Russian officials and elites that many citizens remain indifferent towards the war.
- Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov claimed on November 14 that Russian President Vladimir Putin is personally dealing with issues concerning Ukraine and that he requires no special envoys, likely in response to reports that US President-elect Donald Trump will "soon" appoint a "Ukrainian peace envoy to lead negotiations on ending the war."
- Russian forces advanced in the Ukrainian main salient in Kursk Oblast, west of Ukraine's main salient in Kursk Oblast in Glushkovsky Raion, in the Chasiv Yar direction, and in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area.
- Russian sources are speculating that North Korea may have provided North Korean-produced 170mm M1989 "Koksan" self-propelled artillery systems to Russia. Russian milbloggers published images showing a train transporting alleged North Korean 170mm M1989 “Koksan” self-propelled artillery systems in Krasnoyarsk, Krasnoyarsk Krai.
| 




 [ISW] 러시아의 공세 캠페인 평가, 2024년 9월 29일
[ISW] 러시아의 공세 캠페인 평가, 2024년 9월 29일