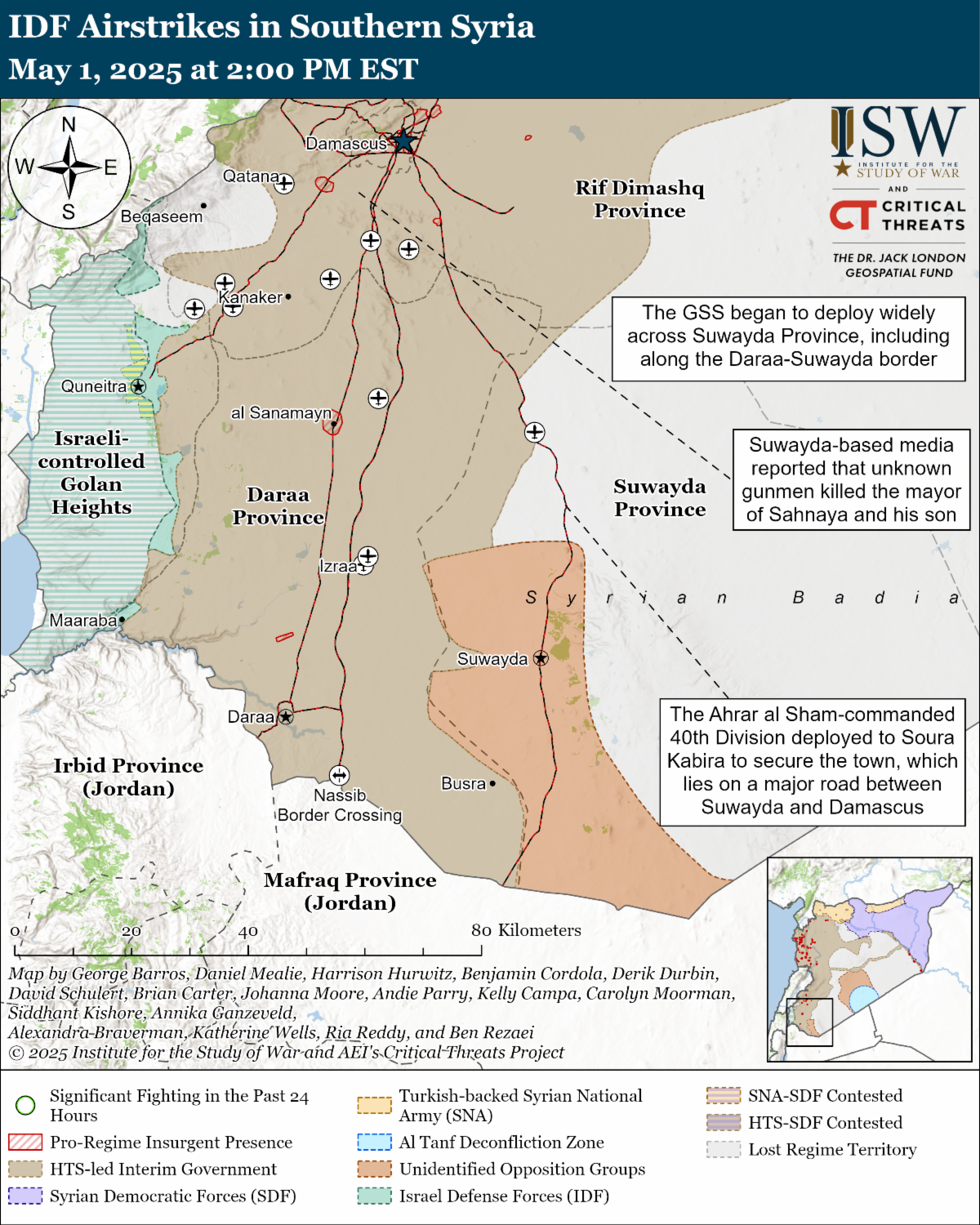
The Israeli prime minister and foreign minister said that Israel would “not allow the [Syrian] Druze ... to be harmed” and threatened additional airstrikes if the violence does not stop, suggesting that Israel aims to pressure the Syrian government into stopping the violence against Druze. An effort to pressure the government to respond as directed assumes that the Syrian government has control over the Sunni fighters attacking Druze communities outside Damascus. Many of these fighters are ad-hoc collections of locals who are attacking the Druze. Some government forces have attacked the Druze. The government deployed General Security Service (GSS) units to cordon off the Druze areas, however, and some of these forces fought alongside local Druze fighters to repulse attacks by Sunni fighters. The government’s deployments alongside local fighters, while other government-linked fighters attack local Druze, suggest that the government does not exert perfect command and control over its forces. The government’s limited control over some extremist elements of its ruling coalition, as well as the localized nature of some of the attackers, indicates that it will be impossible to use airstrikes to pressure the Syrian government into stopping the attacks.
Damascus very likely already wants to stop the violence because the attacks on the Druze make it more difficult to secure the external support Damascus needs to maintain its hold on power. The government faces an extremely dire economic situation and needs external aid and economic support, particularly from the West. Many countries, including the United States and the United Kingdom, have repeatedly emphasized that Syria must prevent violence and hold those responsible accountable. The government will need to convince these countries that the government is deserving of their support.
The airstrikes are unlikely to pressure the Syrian government to stop extremists from conducting attacks. The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) chief of staff ordered the IDF to strike Syrian government targets “if the violence against the Druze does not stop.” The government’s limited ability to demand that extremists stop their attacks means that even if the airstrikes did successfully pressure the Syrian government to make demands of Sunni fighters, it is unclear that government demands would have any effect. The government also has significant capacity issues, and airstrikes targeting the Syrian government will only make government efforts to stop the violence more difficult.
It is unclear how Israel can secure the Druze population in and around Damascus if the airstrikes fail. Airstrikes—if they fail to pressure the government—cannot prevent Druze from being killed or injured by Sunni extremists. Only ground forces prepared to physically defend the Druze communities by force can protect the Druze. It is unclear if Israel is willing or able to protect the Druze in places like Sahnaya and Jaramana, which are roughly 45km and 58km from the Israeli-controlled Golan Heights, respectively. Such a ground operation would be an extremely complex military undertaking. The lack of Druze support for Israeli intervention and the destabilizing effects of a ground operation in Syria mean a ground operation would likely fail and increase the threat to Israel by empowering extremists. Some Druze have protested against Israeli interference in Syria.
Damascus has made serious efforts to curb confessional-motivated violence between Sunni extremists, Druze fighters, civilians, and security services. GSS units reportedly cordoned off Sahnaya and prevented additional external Sunni groups from participating in the clashes targeting Druze militants and civilians. Government officials immediately ordered former Ahrar al Sham commander and 40th Division Commander Colonel Binyan al Hariri (Abu Fares Daraa) to deploy the 40th Division to Soura Kabira to secure the area after fighting between tribal fighters and Druze militiamen along the Damascus-Suwayda highway. Government forces also began to deploy along the border between Suwayda and Daraa provinces on April 1. These deployments follow several attacks that tribal groups launched on Druze towns along the western Suwayda border. Security forces are expected to soon deploy across Suwayda Province. These are tangible steps that suggest that the transitional government appears to be learning how to better contain violence targeting minorities and rebuild local trust since sectarian-motivated violence swept coastal Syria in March 2025.
CTP-ISW defines violence between the Muslim and Druze communities as “confessional” rather than “sectarian” because “sectarian violence” refers to violence between different religious denominations. “Confessional violence” refers to violence between different religions. Most Druze consider themselves a distinct religious group from Islam.
Key Takeaways:
- Israel in Syria: The Israeli prime minister and foreign minister said that Israel would “not allow the [Syrian] Druze...to be harmed” and threatened additional airstrikes if the violence does not stop, suggesting that Israel aims to pressure the Syrian government into stopping the violence against Druze. The airstrikes are unlikely to pressure the Syrian government to stop extremists from conducting attacks, because the government cannot order the extremists to stop. It is unclear how Israel can secure the Druze population in and around Damascus if the airstrikes fail. Airstrikes—if they fail to pressure the government—cannot prevent Druze from being killed or injured by Sunni extremists. Only the formation of a combined Druze-Transitional Government force could successfully secure Druze locals from Sunni extremists while also sidelining pro-Regime elements in the Druze community.
- Violence in Southern Syria: Damascus has made serious efforts to curb confessional-motivated violence between Sunni extremists, Druze fighters, civilians, and security services. GSS units reportedly cordoned off Sahnaya and prevented additional external Sunni groups from participating in the clashes targeting Druze militants and civilians.
- Druze-Damascus Relations: Top Druze leaders continue to engage with the Syrian transitional government, even though Druze Sheikh Hikmat al Hijri publicly denounced the government. This demonstrates the political diversity among Syria’s Druze community.
- Iraqi Politics: Iraqi media reported on May 1 that former Iraqi Parliament Speaker Mohammad al Halbousi and his Sunni rival Khamis al Khanjar formed an election-related agreement that “resembles reconciliation. The recent report about a Khanjar-Halbousi reconciliation is inconsistent with CTP-ISW’s April 28 assessment and could suggest that Halbousi may not be cooperating with the Shia Coordination Framework.
- Houthis and the UN: The Houthis may attempt to pressure the UN into ending the UN Verifications and Inspection Mechanism (UNVIM) by holding oil tankers and cargo ships in Houthi-controlled ports until the UN ends the mechanism.
- Iran-US Talks: The fourth round of US-Iran nuclear talks in Rome on May 3 was postponed.
- Iran-China Cooperation: Iran continued to expand economic cooperation with China to undermine the US maximum pressure campaign.
| 



 [ISW] 이란 업데이트, 2025년 4월 28일
[ISW] 이란 업데이트, 2025년 4월 28일