The West has failed to convince Russian President Vladimir Putin to reevaluate his theory of victory in Ukraine in the past year. Putin’s public statements indicate that he continues to assess that Russian forces will be able to win a war of attrition by sustaining gradual advances along the frontline indefinitely. Putin articulated a theory of victory during the St. Petersburg International Economic Forum (SPIEF) in June 2024 that assumes that Russian forces will be able to continue gradual creeping advances indefinitely, prevent Ukraine from conducting successful operationally significant counteroffensive operations, and win a war of attrition against Ukrainian forces. Putin's assessment that gradual Russian gains will allow Russia to achieve his goals in Ukraine is predicated on the assumption that Ukrainian forces will be unable to liberate any significant territory that Russian forces seize and that the Russian military will be able to sustain offensive operations that achieve gradual tactical gains regardless of heavy losses. Putin's discussion with foreign media at SPIEF on June 19, 2025, demonstrated that Putin still maintains this theory of victory one year later. Putin claimed that Russian forces have a "strategic advantage" in all areas of the front. Putin claimed that Russian forces are advancing along the entire frontline every day and that even if Russian forces advance less on some days, they are "still advancing." Putin claimed that the "situation has changed" since the March 2022 Ukrainian-Russian negotiations in Istanbul and that the terms Russia proposed in 2022 are "much softer" than the terms Russia demands today. Putin threatened that the situation may worsen for Ukraine if Ukraine does not make significant concessions and agree to a peace settlement on Russia's terms and called on Ukraine's partners to "point to the realities of today" to push Ukraine toward a settlement. Putin reiterated that Russia is prepared to achieve its war goals militarily if it is not able to achieve these goals diplomatically. Putin has repeatedly indicated that Russia's war aims include regime change in Ukraine, the installation of a pro-Kremlin proxy government in Kyiv, significant limitations of Ukraine's ability to defend itself against future Russian aggression, Ukrainian neutrality, and NATO's abandonment of its open-door policy.
Putin's theory of victory is predicated on critical assumptions about Ukraine's capabilities and continued Western support for Ukraine — conditions that the West can still change. Putin's theory assumes that Russian forces will be able to leverage their advantages in manpower and materiel to overwhelm Ukrainian forces and that Ukrainian forces will be unable to liberate any operationally- or strategically-significant territory that Russian forces seize. Russian forces are taking disproportionately large manpower losses for marginal tactical gains that are unsustainable in the medium- to long-term, but Putin's theory assumes that the Russian military will be able to maintain the theater-wide initiative and sustain offensive operations that achieve gradual tactical gains longer than the West is willing to provide security assistance to Ukraine and longer than Ukraine's economy and population are able to mobilize for the war effort. ISW continues to assess that Russia will face a number of challenges in its economy and defense industrial base (DIB) in the medium-term that will impede Russia's ability to sustain a prolonged war in Ukraine. Continued rising oil prices following Israeli strikes against Iran may increase Russian revenue from oil sales and improve Russia's ability to sustain its war effort, but only if the price of oil remains high and if Russian oil does not come under additional international sanctions. Increased Western military aid and economic instruments can enable Ukrainian forces to maintain pressure on the battlefield and exacerbate Russia's economic issues, leveraging Russia's weaknesses to achieve a strong negotiating position for Ukraine and the West and extract critical concessions from Russia to bring about a lasting and just end to the war.
Key Takeaways:
- The West has failed to convince Russian President Vladimir Putin to reevaluate his theory of victory in Ukraine in the past year. Putin’s public statements indicate that he continues to assess that Russian forces will be able to win a war of attrition by sustaining gradual advances along the frontline indefinitely.
- Putin's theory of victory is predicated on critical assumptions about Ukraine's capabilities and continued Western support for Ukraine – conditions that the West can still change.
- Putin continued Russia's reflexive control campaign that aims to deter Western provisions of military aid to Ukraine and NATO rearmament but appears to be adapting this campaign for different audiences.
- Putin explicitly stated that he will not sign a peace agreement with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky.
- Putin used his meeting with international journalists to reinject longstanding Kremlin rhetorical lines into the media space, as ISW previously forecasted.
- Russian officials appear to be struggling to posture Russia's economic strength amid increasing signs of a slowing Russian economy.
- Ukraine and Russia conducted the fifth prisoner of war (POW) exchange in accordance the June 2 Istanbul agreements, amid reports that Russia artificially inflated the number of bodies released to Ukraine in previous killed in action (KIA) exchanges.
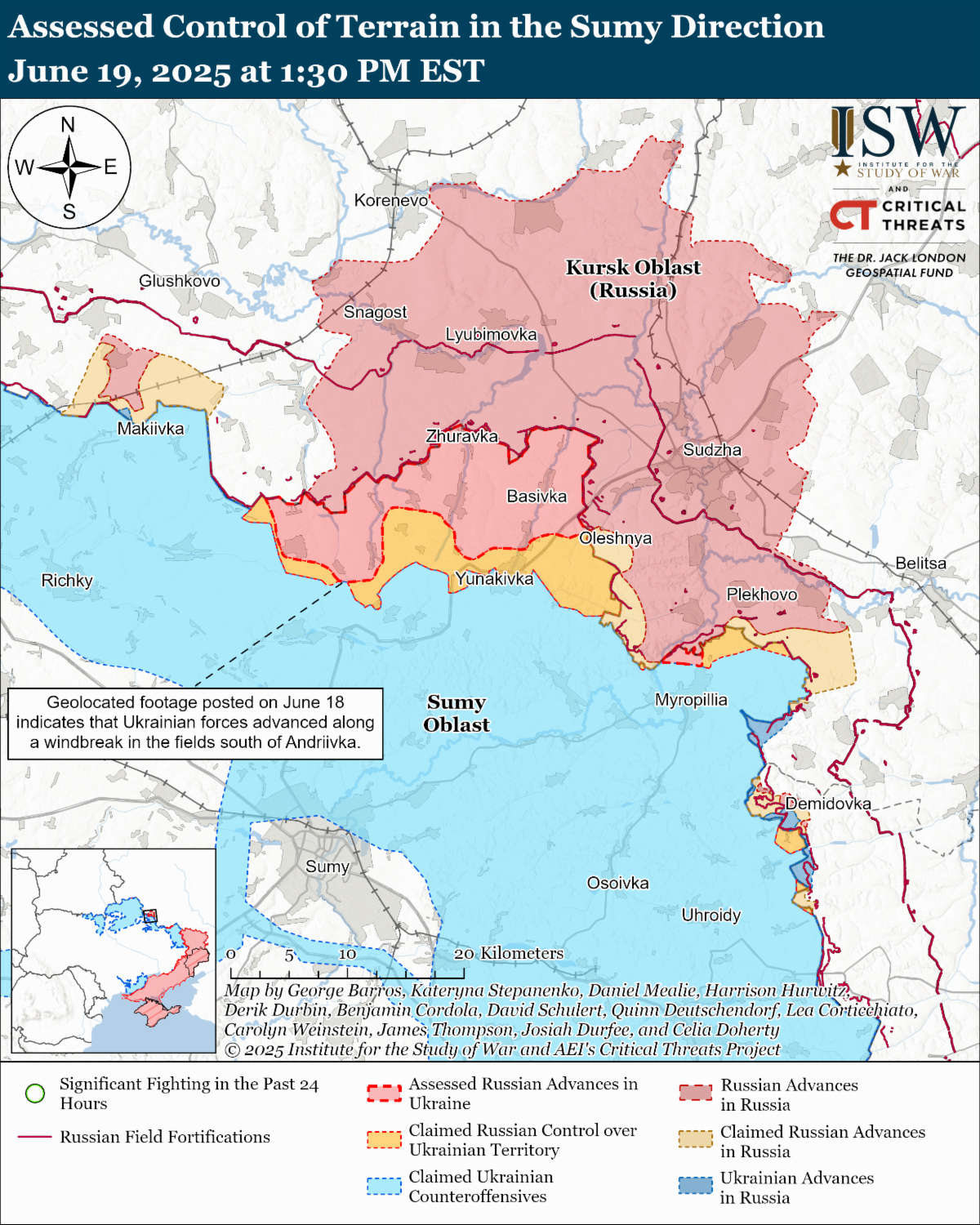
- Ukrainian forces advanced in northern Sumy Oblast. Russian forces advanced near Kupyansk, Toretsk, and Novopavlivka.
| 



 [ISW] 이란 업데이트 특별 보고서, 2025년 6월 19일, 저녁 에디션
[ISW] 이란 업데이트 특별 보고서, 2025년 6월 19일, 저녁 에디션
 [ISW] 이란 업데이트 스페셜 리포트, 2025년 6월 19일, 모닝 에디션
[ISW] 이란 업데이트 스페셜 리포트, 2025년 6월 19일, 모닝 에디션